Application of Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF) in Low-Power Switching Power Supplies (Power < 20W)
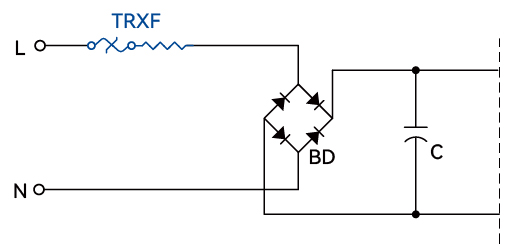
This paper analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of four circuit protection schemes—standalone current fuse, current fuse combined with NTC thermistor, current fuse combined with NTC thermistor and metal oxide varistor (MOV), and wire-wound fusing resistor (RXF)—for overcurrent and overvoltage protection in the main circuit of low-power switching power supplies. It introduces the structure and performance characteristics of the Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF) and verifies its superior protection performance in a smaller current than a direct short circuit scenarios through experimental validation. Finally, the application prospects and standardization needs of TRXF are briefly discussed.
Keywords: TRXF, Low-Power Switching Power Supply, Circuit Protection.
Overview
Compared to linear power supplies, switching power supplies offer significant advantages, including higher capacity, smaller size, lighter weight (only 20%–30% of the volume and weight of linear power supplies), higher efficiency (typically >75%, compared to 20%–30% for linear power supplies), stronger anti-interference capability, wider output voltage range, and modular design. These characteristics make switching power supplies the preferred choice for low-power electronic devices.
A high-quality switching power supply typically comprises the following key components: input grid filter, input rectifier filter, inverter, output rectifier filter, control circuit, and protection circuit. The protection circuit generally includes features such as oad loss protection, overcurrent protection, and overvoltage protection. Without these protective measures, the switching power supply or its load may be damaged or even destroyed due to abnormal conditions, severely impacting device safety and lifespan.
Common Protection Schemes
Overcurrent protection in low-power switching power supplies is primarily achieved by placing overcurrent protection components at the input side. However, with increasingly stringent safety requirements for low-power switching power supplies, relying solely on overcurrent protection is no longer sufficient. Modern low-power switching power supplies require not only reliable overcurrent protection but also robust surge withstand capability, inrush current suppression during startup, and effective protection of smaller current than a direct short circuit to ensure device longevity and safety in complex electrical environments. Currently, the industry commonly employs the following circuit protection schemes for overcurrent and overvoltage protection at the input of low-power switching power supplies:
1. Standalone Current Fuse.
2. Current Fuse Combined with NTC Thermistor.
3. Current Fuse Combined with NTC Thermistor and Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV).
4. Wire-Wound Fusing Resistor (RXF).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Protection Schemes
The aforementioned protection schemes are widely used in low-power switching power supplies, but each has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of electrical performance, installation space, and cost:
| Standalone Current Fuse: Low cost but limited protection functionality.
| Current Fuse Combined with NTC Thermistor: Improves inrush current suppression during startup but offers poor surge and poor protection of smaller current than a direct short circuit.
| Current Fuse Combined with NTC Thermistor and MOV: Enhances surge protection, but increased leakage current in MOVs may pose a fire hazard.
| Wire-Wound Fusing Resistor (RXF): Limited effectiveness in protection of smaller current than a direct short circuit.
To address these challenges, the industry is actively exploring more efficient and safer protection solutions to balance performance, space, and cost requirements.
Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF)
To mitigate the above risks, SETsafe | SETfuse has developed an innovative product: the Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF).
This product integrates a thermal-link within a wire-wound resistor (RXF), achieving:
| EXCELLENT INRUSH CURRENT SUPPRESSION DURING STARTUP.
| ROBUST SURGE PROTECTION.
| SUPERIOR SHORT-CIRCUIT WITHSTAND CAPABILITY AND OUTSTANDING PROTECTION OF SMALLER CURRENT THAN A DIRECT SHORT CIRCUIT.
| COMPACT 2-IN-1 DESIGN FOR OVERCURRENT AND OVERTEMPERATURE PROTECTION.
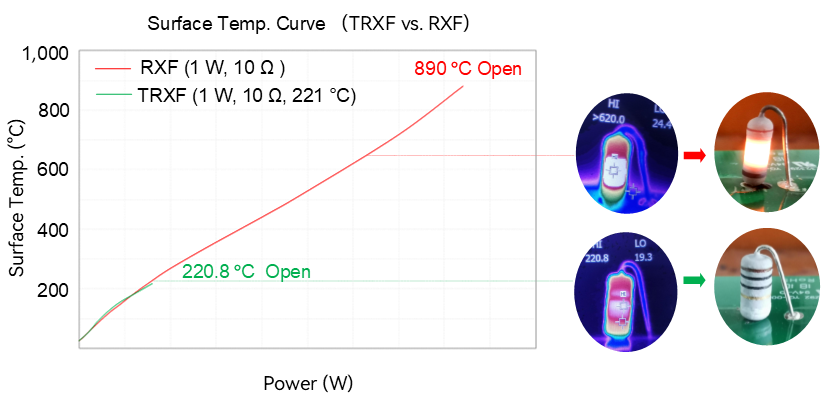
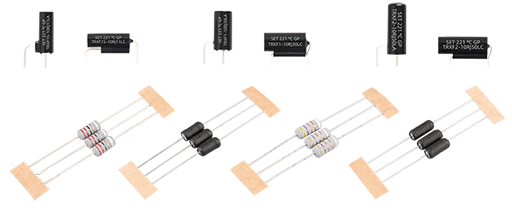
Due to its compact structure, optimized size, and superior performance, Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF) has gained widespread adoption in low-power switching power supplies in recent years. Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF) is a power resistor that combines a thermal-link and a wire-wound fusing resistor (RXF) in series within a single integrated structure, providing both overtemperature and overcurrent protection. The design integrates the overtemperature protection of the thermal-link and the overcurrent protection of the wire-wound resistor (RXF), achieving multiple protection functions in a single device, thereby significantly enhancing system safety and reliability.
Based on similar function, there are two types of structural designs in the market:
External Type:
The thermal-link body is placed adjacent to the wire-wound fusing resistor body, achieving thermal coupling protection through physical contact.
Internal Type (SETsafe | SETfuse Design):
The thermal-link is embedded within the wire-wound resistor, enabling tighter structural integration for improved protection efficiency and faster response times.
For more information, please visit the detailed product page on the SETsafe | SETfuse website:
Thermal-Link & Fusing Resistor (TRXF) Learn more
Industry Applications for Low-Power Switching Power Supplies (<20W)
Devices with power ratings below 20W that may utilize fusing resistors compliant with IEC 60127-8 standards include, but are not limited to (subject to the latest market information):
- Lighting Drivers (LED Bulbs, Spotlights, Dimmable Lights, T8 Tubes, Nightlights) Learn more
- Range Hoods
- Home Network Routers
- Cordless Phones
- Doorbell Transformers
- Tablet Chargers
- DAB Digital Radios
- Charging Strips
- Security And Fire Protection Equipment (Video Surveillance, Smoke Detectors, Smart Locks) Learn more
- Personal Care Devices (Electric Razors, Oral Irrigators) Learn more
- Smart Home Devices (Automatic Curtains, Dimmers, Robotic Vacuum Cleaners, Air Conditioner Panels, Intercom Systems, Smart Speakers, Air Purifiers) Learn more
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production


















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain