Smart Toilet Circuit Safety Protection SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions & Products
| Heated Seat---Over-temperature Protection
| Warm Air Drying System---Over-temperature Protection
| Warm Water Wash System---Over-temperature Protection
| Power Supply, Control Board---Over-voltage Protection
| Power Supply, Control Board---Over-current Protection
Overview
A Smart Toilet (or Intelligent Toilet) is a modern sanitary device that integrates advanced electronic control and sensor technology, going beyond the functions of a traditional toilet to offer enhanced comfort, hygiene, and an intelligent experience. Its core features include rear cleansing, feminine wash, heated seat, warm air drying, automatic deodorization, automatic open/close lid, and night lighting. Some high-end models also include health monitoring functions (e.g., urine analysis, heart rate monitoring) and connectivity with smart home systems. The smart toilet's key advantages are its convenient operation (via remote control or mobile app), water-saving and eco-friendly design, and a personalized user experience that meets demands for health, comfort, and energy efficiency.
Based on function complexity and brand positioning, smart toilets can be categorized into three types: entry-level (basic cleansing and heating), mid-range (adding drying, deodorization, and simple smart control), and high-end (integrating health monitoring, voice control, and AI-powered personalized settings). As of 2025, the global smart toilet market is projected to reach approximately $71.5 billion, with the Chinese market at around 150 billion RMB. By 2030, the global market is expected to grow to $157.2 billion, and the Chinese market is projected to exceed 300 billion RMB, with a CAGR of about 8.8%-11.3%, driven by consumption upgrades, the popularization of smart homes, and increased health awareness. (Market size data is from the internet and for reference only.)

Why Over-temperature Protection is Necessary for Three Circuits in a Smart Toilet
The heated seat, warm air drying, and warm water wash systems in a smart toilet all contain electric heating elements and pose an overheating risk. Therefore, a Thermal-Link is required as a critical safety protection measure. A Thermal-Link is a single-use over-temperature protection component. When the temperature reaches its preset operating temperature, the temperature-sensitive material melts, permanently breaking the circuit to prevent safety incidents caused by overheating. Below are the specific reasons:
Heated Seat---Over-temperature Protection
Function and Risk:
The heated seat maintains a constant temperature (typically 35-45°C) using a heating wire or PTC heating element to provide comfort. If the control circuit fails (e.g., a temperature sensor fault or a stuck relay), the heating element may continue to heat up. If the temperature exceeds a safe threshold (>50°C), it could cause burns to the user, deform or melt the seat material (usually plastic or composite), or even cause a fire.
Role of the Thermal-Link:
The Thermal-Link is installed in series with the heating circuit, close to the heating element. When the temperature rises abnormally, the fuse quickly melts and cuts off the power, preventing further overheating. Its high precision (operating temperature tolerance of ±2°C) and non-resettable feature ensure reliable protection in extreme cases.
Necessity:
The seat directly contacts the human body, making overheating a direct threat to user safety. The Thermal-Link acts as the last line of defense, ensuring that a fault does not lead to serious consequences.
Warm Air Drying System---Over-temperature Protection
Function and Risk:
The warm air drying system uses an electric heater and a fan to produce warm air (typically 40-50°C) for drying. If the fan fails (e.g., rotor lock or blocked air duct) or the control circuit malfunctions, the heater may continue to operate, causing a rapid increase in local temperature (potentially over 100°C), leading to plastic component melting, circuit board damage, or fire.
Role of the Thermal-Link:
The Thermal-Link is placed near the heater. When the temperature exceeds a safe range, it melts and cuts off the heating circuit. Its fast response (<10 seconds) and high reliability ensure the system stops operating immediately under abnormal high-temperature conditions.
Necessity:
The warm air system involves a high-temperature airflow, and overheating could cause a serious safety incident like a fire. The Thermal-Link provides passive protection that complements the potential failure of active controls (like sensors).
Warm Water Wash System---Over-temperature Protection
Function and Risk:
The warm water wash system uses an electric heater to provide warm water (typically 30-40°C) for washing. If the water flow is blocked, the pump fails, or the heater operates in a dry state (without water), the water temperature could become dangerously high (>45°C) or the heater's temperature could surge (>100°C), causing burns, pipe damage, or a fire hazard.
Role of the Thermal-Link:
The Thermal-Link is installed near the heater or the waterway. When an abnormal high temperature is detected, it melts and cuts off the heating circuit, preventing high water temperatures or dry heating from causing an accident. Its compact design is suitable for integration into confined waterway systems.
Necessity:
The warm water directly contacts the human body, and overheating can cause burns. Dry heating can cause equipment damage or fire. The Thermal-Link ensures a safe power cutoff in extreme situations.
These three circuits all involve electric heating elements, and the risk of overheating directly threatens user safety (burns), equipment integrity (material damage), and environmental safety (fire). A Thermal-Link is a passive, reliable, and low-cost protection component that provides final protection when the control system fails, aligning with the safety design philosophy for household appliances.
Standard Certification Requirements
As a household appliance, the smart toilet must meet standards in many countries and regions, which explicitly require heating circuits to be equipped with over-temperature protection devices (such as a Thermal-Link). Below are the relevant countries and standards:
China
GB38448-2025:
Energy Efficiency and Water Efficiency Limits and Ratings for Smart Toilets (Published on August 1, 2025, Effective from April 1, 2027)
GB 4706.1, .53
Require household appliances to have over-temperature protection mechanisms to prevent accidents caused by heating element overheating. The Thermal-Link, as a commonly used protection component, must comply with the relevant test requirements.
GB/T 9816.1-2013 (equivalent to IEC 60691):
This standard specifies the operating temperature (72°C-257°C), breaking capacity (e.g., AC 250V 10A), and test methods (e.g., durability, environmental stress tests) for a Thermal-Link. Smart toilet heating circuits must use Thermal-Links that comply with this standard.
GB/T 23131-2019:
This standard explicitly requires the heated seat, warm water wash, and warm air drying systems to be equipped with over-temperature protection devices (such as a Thermal-Link or a thermostat) to ensure safe operation.
CCC Certification: Smart toilets are included in the CCC certification catalog and must pass safety tests, including verifying the over-temperature protection measures (such as the installation and performance of the Thermal-Link).
International Standards
IEC 60335-2-84:
Requires heating systems (e.g., heated seat, warm water, warm air) to be equipped with over-temperature protection devices. The Thermal-Link is a recommended protection component. This standard is adopted or adapted by many countries.
IEC 60691:
An international standard that governs the design, operating temperature, electrical performance, and test methods for Thermal-Links. It is applicable to certification systems like UL (U.S.), TUV (Germany), PSE (Japan), and KC (South Korea).
UL 60335-2-84 (U.S.):
The North American standard based on IEC 60335-2-84, which requires the heating circuits of smart toilets to have over-temperature protection (e.g., Thermal-Link) and must pass UL certification to meet U.S. market safety requirements.
EN 60335-2-84 (EU):
A European standard requiring the heating systems of smart toilets to have reliable over-temperature protection. The Thermal-Link must comply with IEC 60691 to obtain CE certification.
JIS C 9335-2-84 (Japan):
A Japanese toilet safety specification based on the IEC standard, requiring the use of a Thermal-Link or other protective devices in heating circuits. Products must pass PSE certification.
KS C IEC 60335-2-84 (South Korea):
A Korean standard for smart toilet safety, requiring over-temperature protection and compliance with IEC 60691 for KC certification.
Smart toilet systems for heated seats, warm air drying, and warm water wash must use a Thermal-Link to address overheating risks, preventing burns, equipment damage, or fire. The necessity arises from the high temperatures of the heating elements and their direct contact with the human body. Standards include China's GB/T 9816.1-2013, GB/T 23131-2019, and CCC certification, as well as the international IEC 60691 and IEC 60335-2-84 (which are the basis for UL, EN, JIS, and KS standards), which require heating circuits to be equipped with over-temperature protection. Industry standards (e.g., QB/T 5226-2018, JC/T 2858-2022) provide recommended guidance, while company standards (e.g., ISO 9001, internal brand specifications) further refine the selection and application of Thermal-Links to ensure product safety and market competitiveness.
SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions, Products
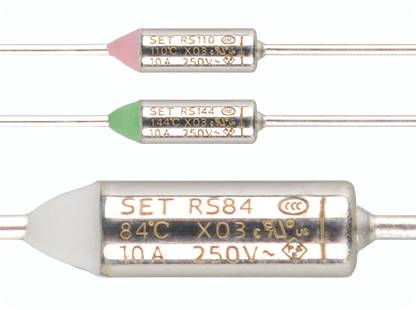



Heated Seat Circuit Protection
Protection Type: Over-temperature Protection
Solution: A Thermal-Link is installed in series with the main circuit of the heating wire or heating film. The Thermal-Link is placed close to the heating element. When the heating element's temperature rises abnormally and reaches the fuse's melting temperature, the Thermal-Link operates, and the circuit is cut off.
Product Name:
Thermal-Link (Organic Type)
Series: RS
Models:
RS72, RS77, RS84 Learn more
Warm Air Drying System Circuit Protection
Protection Type: Over-temperature Protection
Solution: A Thermal-Link is installed in series with the main circuit of the heating wire. The Thermal-Link is placed close to the heating wire. When the heating wire's temperature rises abnormally and reaches the fuse's melting temperature, the Thermal-Link operates, and the circuit is cut off.
Product Name:
Thermal-Link (Organic Type)
Series: RS
Models:
RS110, RS117, RS121, RS128, RS134, RS144 Learn more
Warm Water Wash System Circuit Protection
Protection Type: Over-temperature Protection
Solution: A Thermal-Link is installed in series with the main circuit of the heating rod. The Thermal-Link is placed close to the heating rod. When the heating rod's temperature rises abnormally and reaches the fuse's melting temperature, the Thermal-Link operates, and the circuit is cut off.
Product Name:
Thermal-Link (Organic Type)
Series: RS
Models:
RS77 Learn more
Power Supply, Control Board Circuit Protection
Protection Type: Over-voltage Protection
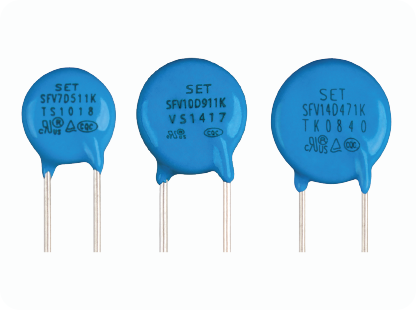
Solution: In the power supply and control board circuits of a smart toilet, especially for over-voltage protection, a Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) is a commonly used component to protect circuits from transient over-voltages (such as lightning strikes or power surges). An MOV is a voltage-sensitive component that has a high impedance in its normal state. When a transient over-voltage occurs, the MOV rapidly changes to a low-impedance state, absorbing the over-voltage energy and protecting the subsequent circuit. When selecting an MOV, parameters like varistor voltage, surge absorption capability, and energy capacity should be considered, and it should be used in combination with other components like fuses, GDTs, and TVS diodes to ensure circuit safety and reliability. The design should also account for environmental factors, thermal management, and safety regulations to optimize protection effectiveness.
Product Name:
Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV)
Series:
SFV7D Learn more
SFV10D Learn more
SFV14D Learn more
Product Name:
Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS Diodes)
Series:
SMA6J Learn more
Product Name:
Gas Discharge Tube (GDT)
Series:
SW Learn more
Power Supply, Control Board Circuit Protection
Protection Type: Over-current Protection
Solution: In the power supply and control board circuits of a smart toilet, a Miniature Fuse plays a key role in safety protection. A fuse is typically installed in series in the circuit. When the current exceeds its rated value, it melts due to overheating and quickly cuts off the circuit, preventing control board damage, equipment failure, or fire risks caused by overload or short circuits. It effectively protects key components like the motor, heater, and sensors, ensuring stable equipment operation and extending its service life while guaranteeing user safety.
Product Name:
Miniature Fuses
Series:
SMD: SCF1032 Learn more
SMD: SCT1032 Learn more
SMD: SCF6125 Learn more
SMD: SCT6125 Learn more
Plastic Case, Through-hole Type. SPF478 Learn more
Plastic Case, Through-hole Type. SPT478 Learn more
Why Choose SETsafe | SETfuse Thermal-Links
| Product Manufacturing: Fully Automated Intelligent Manufacturing.
| Complete Specifications: Maximum Rated Current Up to 30 A.
| Guaranteed Quality: Product Functionality, Performance, and Reliability are Verified.
15 More items than national standards: 30 reliability test items, Including Mechanical, Electrical, Temperature, Soldering, Environmental, and Life Tests.
41.67 Times Higher Than National Standards: Holding Temperature Test Duration is 1,000 hours (National Standard: 24 hours).
2.5 Times Higher Than National Standards: Operating Temperature Accuracy is ±2°C (National Standard: 0/-10°C).
| Multi-System Certifications: Learn more
| Environmentally Friendly Products: HSF (Compliant with RoHS 3.0, REACH, Halogen-Free) Learn more
| Diverse Industry Applications: Learn more
Company Expertise
| Over 25 years of professional design, manufacturing, and sales of circuit protection components. Our products are sold in over 40 countries, and many Fortune 500 companies choose SETsafe | SETfuse. Learn more
Guaranteed, Worry-Free Service
| Pre-sales, in-sales, and after-sales support with professional personnel (feedback within 1 hour) Learn more
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production
Technical Articles (For Reference Only)
Why do Smart Toilets Need Circuit Safety Protection?
As a household appliance that integrates various electrical components, a smart toilet involves electric heating, motor-driven systems, sensor control, and smart connectivity functions. Its operation poses various electrical risks, including overheating, overcurrent, overvoltage, short circuits, and electric leakage. These risks can lead to equipment damage (e.g., melted plastic parts, burnt circuit boards), user safety incidents (e.g., burns, electric shock), or fire hazards. The necessity of circuit safety protection is reflected in the following aspects:
Overheating Protection:
If a heating function (e.g., heated seat, warm water wash, warm air drying) fails, the temperature may exceed safety limits, causing user burns or equipment damage.
Electrical Fault Prevention:
Short circuits or overloads can burn out circuits or cause fires. Protection measures can effectively isolate the fault.
User Safety Assurance:
Prevents high temperatures, electric leakage, or electrical faults from causing direct harm to the user.
Improved Equipment Reliability:
By protecting circuits from abnormal currents or voltage surges, the equipment's lifespan is extended.
Regulatory Compliance:
National and international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60335-1, GB 4706.1) require household appliances to have comprehensive circuit protection mechanisms to ensure market access and user trust.
Which Smart Toilet Functions Require Circuit Safety Protection?
The following smart toilet functions rely on electrical components and need to be equipped with circuit safety protection to handle potential risks:
Heated Seat:
A heating wire or PTC heating element maintains a constant seat temperature (typically 35-45°C). Overheating (>50°C) must be prevented to avoid burns or material degradation.
Warm Water Wash System:
An electric heater provides warm water for cleansing (typically 30-40°C). Dry heating or excessively high water temperatures must be avoided to prevent safety hazards.
Warm Air Drying System:
An electric heater and fan generate warm air (typically 40-50°C). Overheating must be prevented to avoid component melting or fire.
Motor-Driven Systems:
Such as automatic lid opening/closing, nozzle movement, or flush valve control, which need protection against motor overcurrent, rotor lock, or short circuits.
Control Circuits and Sensors:
Including the main control board, temperature/pressure/water level sensors, touch screens, or remote control modules, which need protection from overvoltage, overcurrent, or electrostatic interference.
Additional Functions:
Such as night lighting, deodorizing fans, voice control, or Wi-Fi modules, which need protection against circuit overloads or external voltage surges.
Standards and Certification Requirements
As a household appliance, smart toilets must meet standard certifications in many countries and regions to ensure electrical safety, over-temperature protection, and user safety. Here are the main countries and their corresponding standards:
China
GB 4706.1-2005 (equivalent to IEC 60335-1): "Safety of household and similar electrical appliances - General requirements" - This standard specifies basic safety requirements for electrical insulation, over-temperature protection, and leakage protection.
GB/T 9816.1-2013 (equivalent to IEC 60691): "Thermal-Links - Part 1: Requirements and application guide" - This standard specifies the operating temperature, breaking capacity, and test methods for Thermal-Links to ensure reliable over-temperature protection.
GB/T 23131-2019: "Electronic toilet seats" - This standard specifies requirements for circuit safety, functional performance, and water saving.
CCC Certification: Smart toilets are listed in the CCC certification catalog and must pass safety tests (including circuit protection design) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests before they can be sold.
International Standards
IEC 60335-2-84: "Safety of household and similar electrical appliances - Part 2-84: Particular requirements for toilet seats" - This standard addresses the heating, cleansing, and circuit protection functions of smart toilets. It is used globally, and many countries base their local standards on it.
IEC 60691: "Thermal-Links and application guide" - This is an internationally recognized standard that specifies the design, operating temperature range (typically 72°C-257°C), and performance requirements for Thermal-Links. It is applicable to certifications like UL (U.S.), TUV (Germany), PSE (Japan), and KC (South Korea).
UL 60335-2-84 (U.S.): The North American standard based on IEC 60335-2-84, which emphasizes over-temperature protection and electrical safety. It requires UL certification.
EN 60335-2-84 (EU): A European standard for the electrical safety of smart toilets, which requires CE certification and covers circuit protection and user safety.
JIS C 9335-2-84 (Japan): A Japanese safety specification for toilet seats based on the IEC standard, which requires PSE certification.
KS C IEC 60335-2-84 (South Korea): A Korean safety standard for smart toilets that requires KC certification.
These standards require smart toilet circuit designs to include over-temperature, overcurrent, and over-voltage protection, ensuring that devices do not cause safety incidents under abnormal conditions (e.g., heater failure, grid fluctuations).
Common Circuit Safety Protection Methods and Types
Smart toilet circuit safety protection uses a variety of technical means to provide multi-layered protection against different risks. The following are common protection methods and their coverage of over-temperature, overcurrent, over-voltage, and active protection:
Over-temperature Protection
Thermal-Link:
A single-use protection component that melts and breaks the circuit when the temperature reaches a preset operating temperature (e.g., 94°C, 121°C, 184°C, depending on the model), preventing overheating. Widely used in heated seat, warm water wash, and warm air drying systems.
Bimetal Thermostat:
A reusable temperature control device that breaks the circuit when the temperature exceeds the limit and automatically closes once cooled. Suitable for dynamic temperature regulation.
Temperature Sensor (NTC/PTC Thermistor):
A device that monitors temperature in real-time and, in case of an anomaly, cuts off power or reduces heating power via the main control board.
Overcurrent Protection
Fuse: A device that melts when the current exceeds its rated value (e.g., 3A, 5A), preventing short circuits or overloads from damaging the circuit. Commonly used in the main control board, motor, or heating circuits.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB):
Automatically trips when it detects overcurrent or a short circuit and can be manually reset. Suitable for high-power circuits.
Electronic Overcurrent Protection:
A system that monitors current via the main control board and cuts off power in case of an anomaly.
Over-voltage Protection
Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV):
Absorbs over-voltage caused by grid surges or lightning strikes, protecting the circuit from voltage shocks.
Gas Discharge Tube (GDT):
Used for high-voltage surge protection, often combined with an MOV.
Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) Diode:
A device that quickly responds to transient over-voltage, protecting sensitive electronic components (e.g., control chips, sensors).
Active Protection
Smart Monitoring System:
A system that uses a microprocessor and sensors (e.g., temperature, current, water level sensors) to monitor the device's status in real-time. In case of an anomaly, it automatically cuts off power or adjusts the operating mode. For example, it can turn off the heater when a dry-heating risk is detected or pause washing if the water temperature is too high.
Residual Current Device (RCD / GFCI):
A device that detects leakage current (e.g., above 30mA) and quickly cuts off power to prevent electric shock, which is especially important in the wet environment of a bathroom.
Software Protection Mechanism:
A mechanism that sets safety thresholds (e.g., a maximum temperature of 50°C, a maximum current of 5A) via firmware, triggering a power cutoff, power reduction, or an alarm in case of an anomaly.
Comprehensive Application:
Smart toilets typically use a multi-layered protection strategy. For example, a Thermal-Link can be combined with a smart monitoring system to provide both hardware (passive) and software (active) protection. The Thermal-Link serves as the final protection for critical heating circuits, while the smart monitoring system intervenes proactively, reducing the probability of a fault occurring.
Summary
Smart toilets require circuit safety protection to handle risks from overheating, overcurrent, over-voltage, and electric leakage, protecting functions such as the heated seat, warm water wash, warm air drying, motor-driven systems, and control circuits. Common protection methods include Thermal-Links, thermostats, fuses, MOVs, RCDs, and smart monitoring, which cover over-temperature, overcurrent, over-voltage, and active protection. Chinese standards include GB 4706.1-2005, GB/T 9816.1-2013, GB/T 23131-2019, and CCC certification, while international standards like IEC 60335-2-84 and IEC 60691 are followed, and regional certifications include UL, CE, PSE, and KC. These standards ensure product safety and global market compliance.


















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain